Table of Contents
Introduction
Japan is a technologically advanced country with a rich cultural history. Its third-largest economy after the US and China makes it a preferred destination for professionals looking for great work opportunities and financial growth.
Did You Know?
Many Japanese companies offer annual incentives, known as “bonuses,” which can amount to one or even two months of salary in addition to the base salary.
The average monthly salary in Japan is around 515,000 Japanese yen. Salaries can range from a low average of 130,000 yen to a high average of 2,300,000 yen.
However, the actual maximum salary is even higher than this highest average.
Japan plays a big role in the world’s economy. It is well-known for its successful car industry and ability to adapt to changing markets.
This unique country mixes tradition with modern life and offers a high standard of living.
If you plan to move to Japan or already live there, understanding the salary levels can help you manage your life better.
This blog post will explain the salary structure in Japan in detail. It will give you helpful information to plan your life properly in this country.
Let’s dive in.
Understanding Average Salary in Japan
Average salary means the total amount of money people earn divided by the number of people.
Japan, a major player in the world economy, stands out with a strong emphasis on industries like
- Automobiles
- Technology
- Innovation
It is an ideal ground for business growth and an emerging hub for outsourcing ventures.
Curious about the expenses involved in hiring a Japanese workforce?
As of May 2023, the average annual salary in Japan is 6,170,000 Japanese Yen (JPY) or around 45,453 USD.
This figure provides a snapshot of the labor market’s financial landscape, making Japan a noteworthy consideration for companies looking to expand or outsource.
It’s important to note that the cost of living in Japan can also affect how far a salary goes. For example, living in Tokyo might be more expensive than in other parts of the country.
Average Salary in Japan: Stats & Trends
The average pay in Japan exhibits regional disparities influenced by factors such as:
- Job location
- Work experience
- Education level
When considering these elements, Salary Explorer indicates that the monthly salary (average) in Japan is around 515,000 Japanese Yen (JPY), equivalent to approximately 3,794 US Dollars (USD).
This figure includes the basic salary and additional benefits such as housing and transport.
These supplementary perks contribute to the total compensation package, augmenting employees’ overall financial well-being.
Additionally, the evolving work culture in Japan, with a growing emphasis on work-life balance and employee satisfaction, further impacts the dynamics of salary trends.
Now, let’s see several other aspects of the average salary in Japan.
1. The Average Japanese Salary Range
The monthly salary for people working in Japan can vary widely, ranging from around 130,000 Japanese Yen (958 USD) to 2,300,000 JPY (16,944 USD).
It’s important to note that the upper range represents the highest average salary, not the maximum that someone can earn.
2. The Median Salary
The median salary in Japan for 2023 is 471,000 JPY (3,470 USD) per month.
The median is like the middle point – half of the people in Japan earn more than this, and the other half earn less.
Employers often consider offering pay around the median when hiring for specific jobs.
3. The Minimum Wage
Japan follows a 40-hour workweek, and each region’s Minimum Wage Council determines the minimum hourly wage.
The national average minimum wage is 931 yen, which increased to 961 yen in April 2023.
People who work more than the standard hours should get extra pay according to the Labor Standards Act.
Tokyo has the highest minimum wage in Japan in USD, about 985 JPY (8.5 USD) per hour, comparable to wages in high-income cities like Hong Kong and Seoul.
This difference is because Tokyo has more businesses and better infrastructure.
What is the Annual Salary Incremental Rate in Japan?
In Japan, workers typically get a salary increase of around 8% every 16 months.
This 16-month time frame is because performance evaluations don’t always happen exactly once a year.
The increase can change depending on the industry and how much experience a person has.
When you’ve been working for a while, companies might give you a higher salary to encourage you to stay and keep using your skills.
Here, we will look at the annual increments in Japan based on the following:
- Experience
- Industry
1. Annual Increments Based on Experience
Here are the annual increments in Japan as per experience:
| Experience Level | Annual Increment |
| Top Management | 15%-20% |
| Senior | 10%-15% |
| Mid-career | 6%-9% |
| Junior | 3%-5% |
Source: Salary Explorer
2. Annual Increments Based on Industry
Here are the annual increments in Japan as per experience:
| Industry | Annual Increment |
| Education | 2% |
| Construction | 3% |
| Travel | 4% |
| Healthcare | 5% |
| Information Technology | 6% |
| Energy | 7% |
| Banking | 8% |
Source: Salary Explorer
Top 4 Factors Affecting Salaries in Japan
Here are some major factors that affect salaries in Japan:
1. Region
In Japan, where you work can significantly impact your salary.
Different regions have varying living costs, with cities like Tokyo generally offering higher salaries compared to other cities.
Housing prices, transportation costs, and overall economic activity in each area influence this regional difference.
| City | Average Salary/ Month |
| Okinawa | 390,000 JPY (2,873 USD) |
| Hiroshima | 476,000 JPY (3,507 USD) |
| Saitama | 486,000 JPY (3,580 USD) |
| Kawasaki | 495,000 JPY (3,647 USD) |
| Kyoto | 505,000 JPY (3,720 USD) |
| Fukuoka | 526,000 JPY (3,875 USD) |
| Nagoya | 545,000 JPY (4,015 USD) |
| Osaka | 555,000 JPY (4,089 USD) |
| Yokohama | 564,000 JPY (4,155 USD) |
| Tokyo | 574,000 JPY (4,229 USD) |
2. Education Level
Your level of education plays a crucial role in determining your salary in Japan.
Generally, individuals with higher education qualifications tend to earn higher salaries.
Completing advanced degrees or specialized training can enhance your skills and make you more valuable in the job market, leading to better-paying opportunities.
Here is the salary growth rate in Japan based on education level:
| Education Level | Salary Increase (%) |
| High School | – |
| College or Diploma | +17% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | +24% |
| Master’s Degree | +29% |
| Ph.D. | +23% |
Source: Salary Explorer
3. Experience Level
The number of years you’ve worked, your job experience, and the skills you’ve gained over time all contribute to your salary in Japan.
Generally, individuals with more experience in a particular field are rewarded with higher salaries.
Here’s how the average salary increases in Japan with experience:
| Experience Level | Salary Increase (%) |
| Less than 2 years | Starting Salary |
| 2-5 years | 32% Higher Than 0-2 years |
| 5-10 years | 36% Higher Than 0-5 years |
| 10-15 years | 21% Higher Than 0-10 years |
| 15-20 years | 14% Higher Than 0-15 years |
| Above 20 years | 9% Higher Than 0-20 years |
Source: Salary Explorer
Companies recognize the value of seasoned employees who bring expertise and a deep understanding of their roles.
In Japan, most companies expect their employees to retire when they turn 60. However, some retired workers seek part-time jobs because they don’t start receiving their Japanese pension until they reach the age of 65.
4. Industry
The industry you work in significantly impacts your salary.
Specific sectors like technology, finance, and engineering tend to offer higher salaries than others.
Industries requiring specialized skills or in high demand often pay more to attract and retain top talent.
Let’s look at the average salaries in Japan based on industry:
| Industry | Average Annual Salary |
| Finance and Accounting | 6,360,000 JPY (46,853 USD) |
| Education | 6,550,000 JPY (48,252 USD) |
| Real Estate | 6,990,000 JPY (51,494 USD) |
| Science and Technical Services | 8,270,000 JPY (60,923 USD) |
| Medical and Health Care | 9,220,000 JPY (67,921 USD) |
It’s essential to consider the specific dynamics and demands of the industry when evaluating salary expectations.
Understanding these four factors — region, education level, experience level, and industry — is essential for individuals navigating the Japanese job market.
Tailoring your career path, acquiring relevant skills, and considering the regional context can all contribute to negotiating a competitive salary in Japan.
Tips for Negotiating Salaries in Japan
Here are some significant tips for negotiating salaries in Japan:
1. Research First: Before discussing salary, research typical pay for your job in Japan. Knowing this helps you understand what’s fair, especially when applying for Visa sponsorship Japan jobs.
2. Politeness Matters: Japanese culture values politeness. When negotiating, be respectful and considerate. It’s common to express your thoughts modestly.
3. Consider the Entire Package: Don’t just focus on the salary number. Consider other benefits like bonuses, health insurance, and vacation days. The overall package is crucial.
4. Understand Company Culture: Learn about the company’s culture. Some places might have a more formal structure, and others may be open to negotiation. Adapt your approach accordingly.
5. Highlight Your Value: During negotiations, emphasize how your skills and experience will benefit the company. Show them why you’re worth the salary you’re proposing.
6. Be Patient: Negotiations might take time. Be patient and open to discussion. Rushing may not be viewed positively.
7. Know When to Stop: Understand when to stop negotiating. Pushing too hard can be counterproductive. If the company is firm, consider other aspects like career growth opportunities.
8. Consider Cost of Living: If you’re moving to a different city, consider the cost of living there. Negotiate a salary that aligns with the living expenses in your new location.
9. Seek Guidance: If possible, seek advice from local colleagues or professionals who understand the Japanese work culture. They can offer insights into effective negotiation strategies.
10. Express Gratitude: Regardless of the outcome, express gratitude for the opportunity. Being appreciative contributes positively to your professional image.
Remember, negotiating salaries is a two-way conversation.
Be prepared, stay positive, and find a balance that works for both you and the company.
Highest and Lowest-Paying Professions in Japan
It’s time to explore the average salaries in Japan based on professions.
1. Lowest Paying Professions
Here is the list of professions that earn the lowest in Japan:
| Job Title | Average Salary per Month |
| Human Resources Officer | 331,000 JPY (2,438 USD) |
| Retail Cashier, Call Center Representative | 207,000 JPY (1,525 USD) |
| Nursery Teacher, Automotive Mechanic | 203,000 JPY (1,495 USD) |
| Customer Service Representative | 201,000 JPY (1,481 USD) |
| Waiter | 163,000 JPY (1,201 USD) |
Source: Salary Explorer
2. Highest Paying Professions
Here is the list of professions that earn the highest in Japan:
| Job Title | Average Salary per Month |
| Dietitian | 1,020,000 JPY (7,514 USD) |
| Attorney | 1,080,000 JPY (7,956 USD) |
| Chief Financial Officer | 1,150,000 JPY (8,472 USD) |
| Chief Executive Officer | 1,220,000 JPY (8,987 USD) |
| Dentist | 1,290,000 JPY (9,503 USD) |
Source: Salary Explorer
Many foreigners in Japan like working as English teachers, which is a popular job. The average starting salary for this job is around 200,000 Japanese Yen, which is about 1,473 US Dollars.
Salary Management with Workstatus
Workstatus is a helpful tool for companies to understand more about their employees and how they work.
It looks at various aspects such as work hours, tasks, and productivity, aiding organizations in making informed decisions about employee salaries.
Here’s how Workstatus can assist you in creating a fair salary structure for your employees, taking into account their skills, work hours, performance, attendance, and more:
1. Online Timesheets: Workstatus allows employees to log their work hours online easily. It makes tracking how much time they spend on different tasks and projects is simple.
2. Overtime Tracker: The Overtime Tracker helps employers monitor and manage employees’ extra work hours. It makes sure that everyone is compensated fairly for any additional time they put in.![]()
3. Attendance Tracking: Keeping a record of your employees’ attendance becomes straightforward with Workstatus. This feature simplifies employee scheduling and ensures that everyone is present when needed.
4. Habit Tracker: The Habit Tracker lets employers monitor employee habits and routines. This not only promotes a healthier work-life balance but also boosts overall productivity.
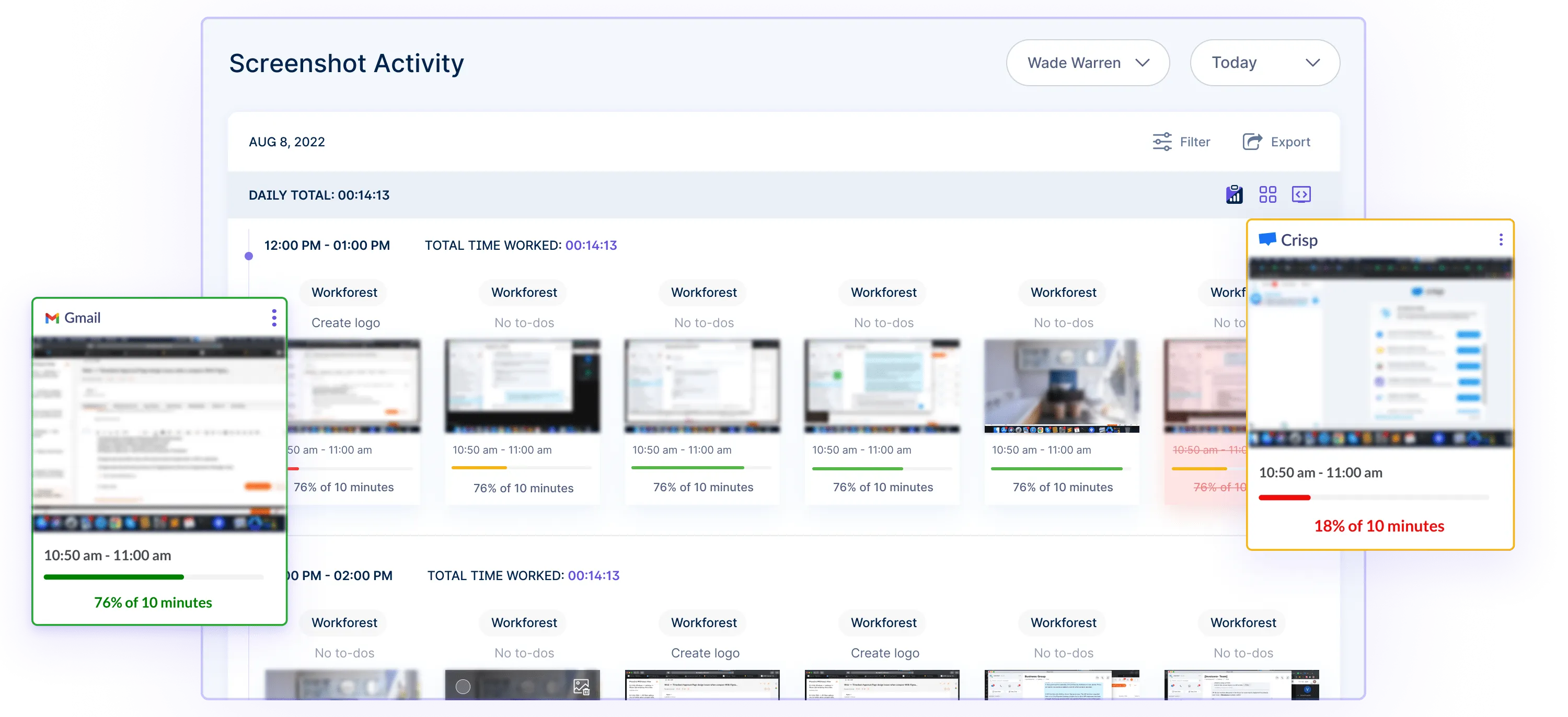
5. Performance Tracking: Companies can assess employee performance using predefined metrics. It helps recognize top performers, facilitating decisions about salaries and appraisals.
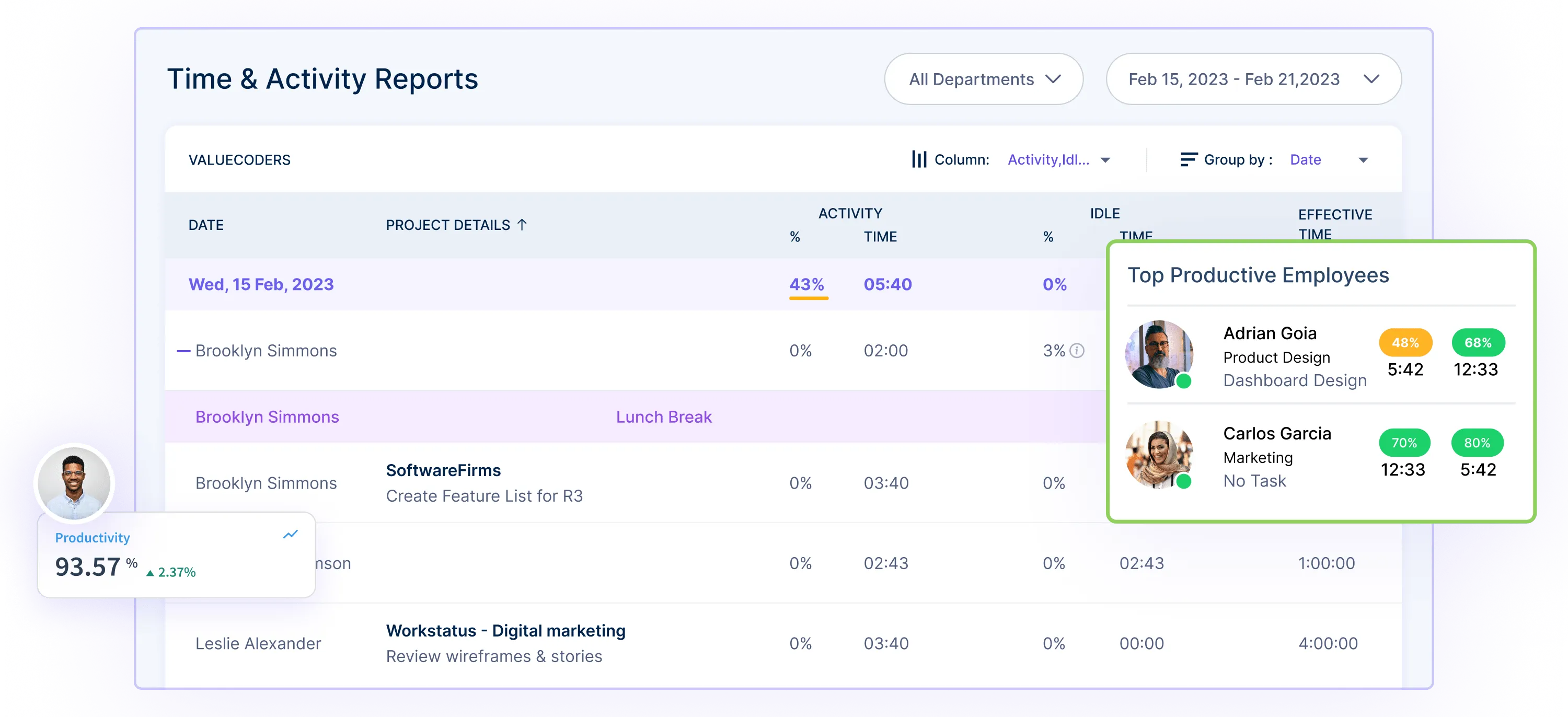
6. Automated Reporting System: Workstatus includes an Automated Reporting System that generates comprehensive reports based on collected data. It simplifies analyzing employee information, making it easier for companies to make informed decisions about salary structures and rewards.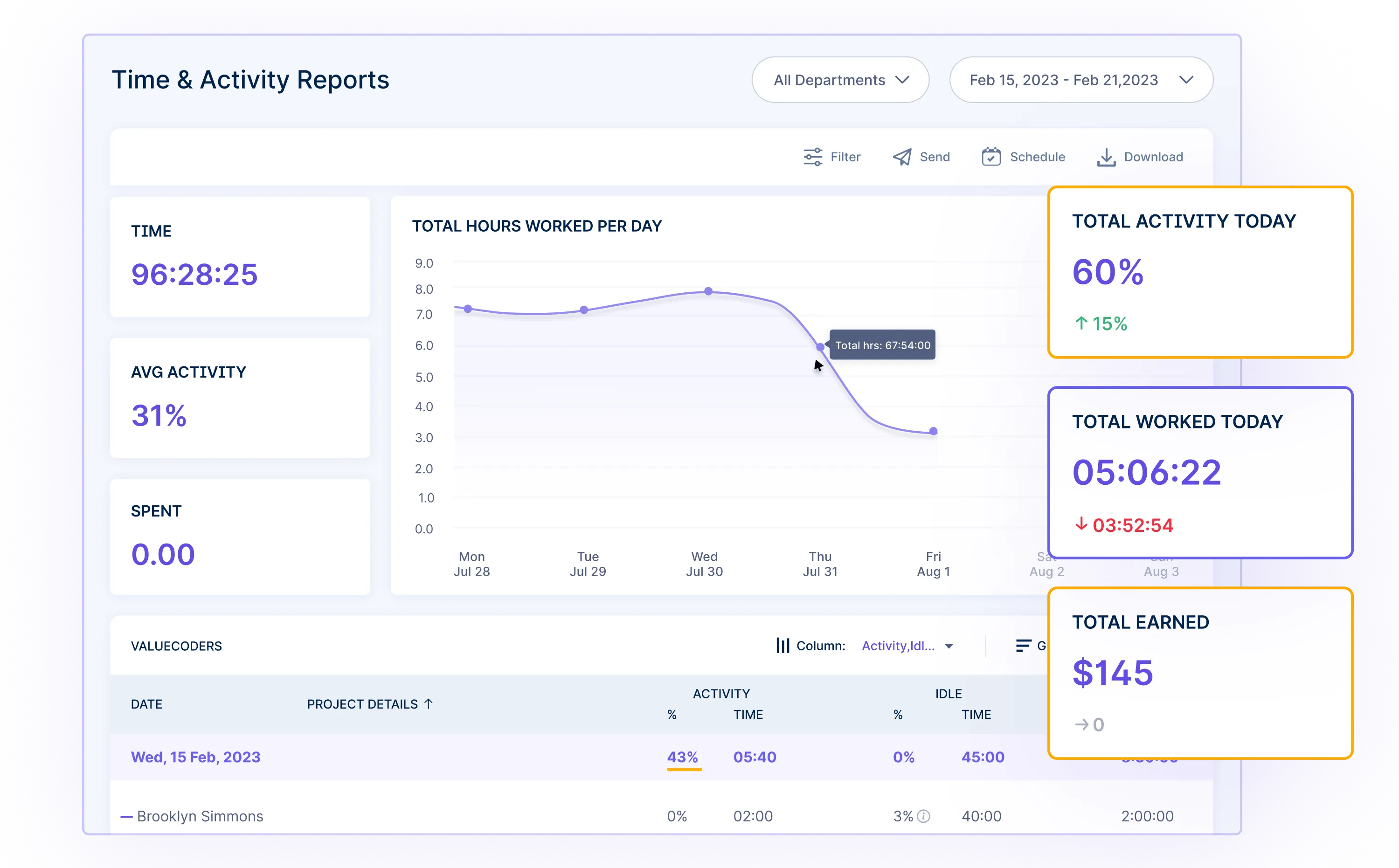
Closing Thoughts
Hiring new employees in Japan when they’re just starting out is not too expensive.
They usually get paid a minimum of 30,400 to 39,600 Japanese Yen per month, which is about 224 to 292 US Dollars.
But, if you need more experienced people or for jobs that are a bit tricky, the cost of employees can go up.
Even with the costs, Japan is a good place to consider if you want to get work done through outsourcing.
At last, exploring the Japanese job market can offer cost-effective solutions for your business needs, making it a promising destination for outsourcing endeavors.