Table of Contents
Earlier, the agile project management approach was used by small, self-contained teams working on small projects. They strived to make the agile mode work for the betterment of software makers worldwide.
As a result, agile project management has gained immense popularity, leading more companies to scale agile beyond single teams or projects. It has even spread across development teams like IT, business development, marketing, and more.
Did You Know?
On average, organizations that adopt Agile project management methodologies experience a 37% increase in project success rates.
So, agile project management is less restrictive than other traditional project management techniques. It allows the team to adjust to changing conditions or project requirements as necessary.
In this blog, we will learn about agile project management in detail.
Let’s get into it!
Introduction to Agile Project Management
What Is Agile Project Management?
Agile project management is a methodology that emphasizes segmenting the overall project lifecycle into smaller tasks and more manageable timeframes. It prioritizes the delivery of a working product throughout the process rather than project deliverables and products at the end. This enables the project team and stakeholders to collaborate closely during the project execution while providing feedback, not just during the project post-mortem.
Agile offers the freedom to modify and iterate throughout the development process, which is necessary given that today’s customers and organizations demand quick reactions and modifications. Agile project management is a fundamental component of DevOps methodologies, which integrates development and operations teams.
Principles of Agile Model
Here are the key principles of agile model:
1. Accept Modifying Requirements
Change requests should still be welcomed if necessary, even in the last stages of project execution. The Agile principle states in its original form that your team must “welcome changing requirements, even late in development.” Agile methods leverage change to benefit the client’s edge over competitors.
2. Cooperation
To complete a project successfully, agile demands that clients, stakeholders, and developers collaborate (sometimes in the same room). This lowers the risk that comes with developing a project by fostering better collaboration and communication.
Furthermore, management finds it easier to comprehend the difficulties developers encounter and the effects of changes made to development when they are more closely involved in the process.
3. Iterative and Incremental
Agile project management is highly iterative and incremental. Projects are broken down into multiple concrete segments (iterations). Within these iterations, progress is measured in small, tangible increments.
Business objectives aren’t isolated to one iteration—it’s about measuring continual progress on a project-by-project basis.
By establishing concrete goals at each stage, projects are continuously revised to fit new requirements and market demands (incremental).
That way, teams can assess if it makes sense to pursue a given direction or move on to another solution that better fits client or customer needs.
4. Monitor and Track the Progress of the Project
It becomes essential to take detailed notes daily so that you know how far along you are in completing each task. If you don’t write things down, it may be difficult to remember what you achieved or what has not been started yet.
Monitoring and tracking your progress also allows you to make changes if something is not working properly.
In agile project management, it is important to allow for quick changes during a sprint because, often, minor tweaks are made along the way that make your project much better.
These quick changes are sometimes referred to as smoke-testing, meaning they have little risk of introducing severe issues into a sprint and allow teams to correct small problems before they become larger ones quickly.
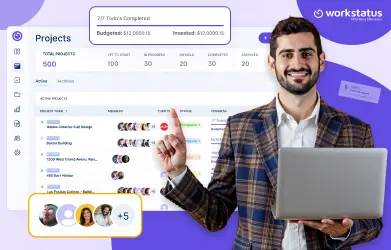
Sign up to try the best project budgeting software to track the progress of your projects in an efficient and effective manner.
5. Self-Organizing Teams
This one is all about communication. With a self-organizing team, you have a team that doesn’t have specific roles, but you trust them to work together. They rarely require anyone to tell them what to do or how to act, and they are free to approach challenges as they see fit.
Communication is key here; make sure everyone is on board with each decision made and clear on what they should be working on at any given time.
It can be especially important when you first implement a self-organizing team structure.
Things will get smoother over time, but there’s nothing wrong with that, even if things get bumpy!
6. Face To Face Interaction with the Development Team
In agile management, there is no replacement for face-to-face interaction between the development team and the client.
Effective communication must happen in real-time and, when necessary, face-to-face—even if it requires an extra trip to a meeting room. Missing either communication or active participation can jeopardize the success of the project. To streamline agile processes and ensure alignment, leveraging a robust IT project management software is essential.
To avoid delays and errors on your next project, don’t cut corners by leaving out communication with your team members.
A physical presence also means that parties are held accountable for their work.
7. Functional Software
If you swap out “software” for “products,” you’ll discover that the principles are rather self-explanatory and can be applied to any project that has ever been created. This principle was developed due to the IT industry’s overly formalized processes and documentation hampered innovation.
Having functional software is the main indicator of development. In different industries, this idea could be summarized as follows: “A working product is more valuable than a checklist.” Models, requirements analysis papers, and mock-ups could be helpful, but they won’t be very helpful if you can’t turn this data into a functional product.
Both business owners and project managers should concentrate on reducing paperwork and increasing productivity. Unfinished goods are inventory, and inventory is wasteful spending.
Steps in Agile Development Management

Step 1: Ideation
The ideation phase is the first step in any productive Agile software development project. Future app users, developers, business team, and stakeholders are all closely collaborated with by the Agile product owner (PO). With the help of the larger team, the PO assembles a project vision by:
- Specifying the new software’s objective and purpose
- Identifying and recording user and business requirements
- Setting priorities for activities and assigning resources
Step 2: Development
After ideation, teams can begin developing the first software iteration. The development phase includes all associated production tasks in the SDLC, including coding, architecting, and UX/UI design.
In the Agile application development lifecycle, the initial iteration of a software product’s development is frequently the longest.
Step 3: Testing
The team is pleased with the first iteration of the software, and development proceeded without a hitch. The app must pass a quality assurance review before being released. To make sure the app is fully working, the Agile team tests it by:
- Verifying the cleanness of the code
- Fixing flaws and mistakes
- Conducting trial runs
Step 4: Deployment
The Agile team releases the program to an on-premises server or the cloud when it’s ready for public release.
The product is live and available to clients as soon as it is launched. In the SDLC, deployment is typically the most joyful phase: you made it! Give yourself a pat on the back now, but you still have one step left.
Step 5: Operations
The work doesn’t stop after the magic button is pressed. Continuous maintenance keeps functionality intact and helps crush bugs. There will be chances for feedback collection and feature enhancements to be released in subsequent versions of the app as people interact with it.
Top 6 Benefits Of Agile Project Management
Here are the six benefits of employing agile project management:
1. Superior Quality Product
Testing is integrated within the project execution phase in agile project management, which results in a higher overall product quality. The customer is kept informed throughout the development process and has the right to request modifications based on the market’s needs. Agile is an iterative process, so over time, self-organizing teams continue to learn, develop, and improve.
2. Better Control
The Agile methodology offers managers greater control over their projects through its emphasis on transparency, feedback integration, and quality control measures. Quality control is maintained during the project’s implementation phase using sophisticated reporting tools and procedures, and daily progress updates are provided to all stakeholders.
3. Enhanced Project Predictability
Enhanced visibility facilitates risk prediction and the development of efficient mitigation strategies. There are many techniques to recognize and anticipate risks within the Agile framework, and to prepare ahead to make sure the project goes as planned.
For instance, the Scrum tools makes the project more visible by using burndown charts and sprint backlogs, which enables managers to forecast performance and make appropriate plans.
4. Reduced Risks
Any project employing the Agile technique should, in theory, never fail. Agile employs brief sprints with an emphasis on continuous delivery. Even in cases where a particular strategy does not work out as planned, there is always a tiny portion that may be saved and utilized later.
5. Continuous Improvement
Developing introspection and aiming for ongoing enhancement is among the top fundamental tenets of the Agile manifesto. Because the process continues, every sprint will build upon the prior one and avoid repeating mistakes. Agile approaches encourage a collaborative and open culture of ideas, allowing team members to grow from one another’s experiences and learn from one another.
6. Boosted Team Morale
Agile teams have more freedom and decision-making power since they are self-organizing and self-managing. The project manager protects the team from management and sponsor meddling.
The teams’ cross-functional structure aids members’ professional development and acquisition of new project management techniques. The team meets often to discuss obstacles and progress, improving teamwork. Agile fosters a close-knit community where teams can have adaptable team structures because of the small team sizes.
Agile Project Management Frameworks
Kanban Framework
Kanban is a framework for managing Agile projects. It is based on the theory that work should flow through a process continuously, which is visualized as a series of lanes or columns on a board.
The Kanban system starts with the assumption that teams will always work on over one project at a time and that it’s not possible to predict in advance how much work will be available.
The goal of Kanban is to ensure that the right items are being worked on at the right time by limiting the number of items that are in progress (to avoid overwhelming team members) and by indicating when new work should be started.
Kanban boards can be used for both software development and non-software projects. Individual team members can also use them to visualize their own work or the whole team to see the status of all ongoing work.
Scrum Framework
The Scrum Framework is one of the most popular Agile Project Management frameworks. It’s a time-boxed framework that helps teams manage complex projects.
It comprises three key roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Team), five ceremonies (Sprint Planning Meeting, Daily Scrum Meeting, Sprint Review Meeting, Sprint Retrospective Meeting, and the Release Planning Meeting), and three artifacts (Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Burndown Charts).
The Scrum Master ensures that the team should follow the framework and stays on track.
The Product Owner is responsible for creating and managing the Product Backlog. And finally, the team is responsible for delivering working software for each Sprint.
Hybrid Framework
The Hybrid framework combines both traditional and Agile approaches and can be customized to fit the specific needs of your project. Such flexibility is one of the major benefits of the Hybrid approach.
Traditional management frameworks are very linear, with rigidity built into the process. This can often lead to projects becoming bogged down and delayed, as changes cannot be easily made once the project has begun.
In contrast, Agile methods are designed to be more flexible, allowing constant change and adaptation as the project progresses.
The Hybrid framework takes the best of both worlds, combining the linear structure of traditional management with the flexibility of Agile.
It allows for a project to be planned and executed more flexibly while still maintaining the benefits of conventional methods.
Lean Framework
The Lean framework is based on continuous improvement and waste reduction principles. Its goal is to help project managers deliver value to their organizations efficiently and effectively.
The Lean framework comprises four core practices:
- Set Kaizen Events
- Conduct Daily Stand-up Meetings
- Perform Queueing Analysis
- Manage Work In Progress limits
These practices help project managers constantly identify opportunities for improvement and ensure that work is flowing smoothly throughout the organization.
Closing Thoughts
All in all, agile project management is a cutting-edge methodology for projects of all kinds, not only software ones.
It gives teams the adaptability to react to changes throughout the development lifecycle, enabling them to deliver more customer-focused solutions of higher quality.
Agile promotes continuous development through empowering teams, increasing accountability, and stimulating creativity. It enables you to adapt to change without losing your bearings, which is fantastic for any program, too.